Unlocking Effective Learning: A Guide to Outcomes
Want to create training that truly sticks? This listicle provides practical learning outcomes examples to help you define exactly what your students should achieve. Understanding different types of learning outcomes—from Bloom's Taxonomy to Backward Design—is key to developing effective courses and workshops. We'll cover seven types of learning outcomes examples, showing you how to create more engaging and impactful learning experiences. This guide will empower you to craft training that delivers measurable results for your Shopify or arts and crafts business.
1. Bloom's Taxonomy Learning Outcomes
Creating effective learning experiences, whether for training employees, educating customers about your product, or designing workshops for fellow crafters, requires a clear understanding of what you want your audience to achieve. Bloom's Taxonomy provides a robust framework for defining learning outcomes, ensuring that your educational content leads to meaningful results. It offers a hierarchical structure of cognitive skills, ranging from basic recall to complex creative processes. This system allows you to design learning experiences and assessments that progressively develop deeper understanding and higher-order thinking skills in your target audience.
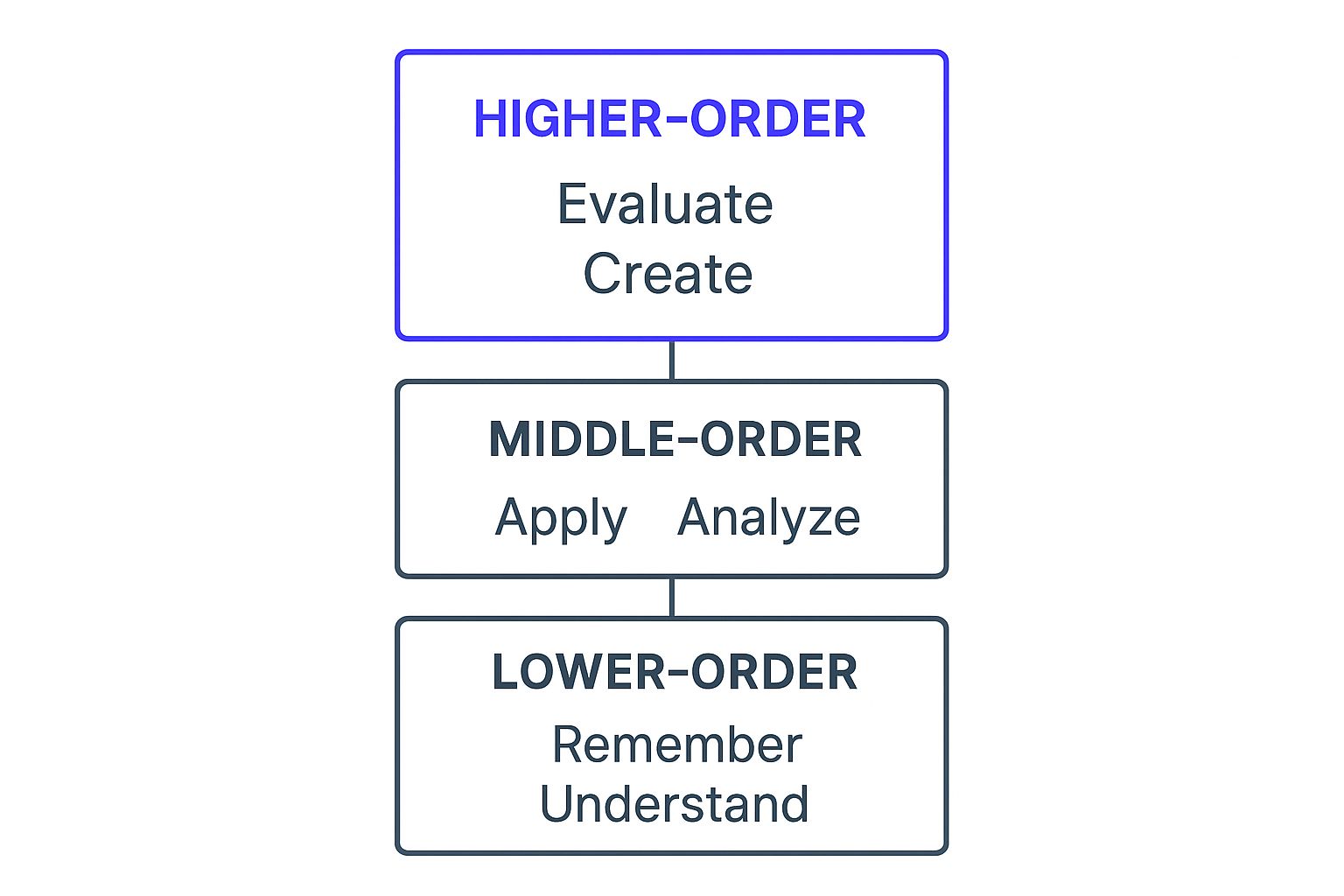
The infographic visually represents the hierarchical nature of Bloom's Taxonomy, with "Creating" at the top, representing the highest level of cognitive processing, and descending through "Evaluating," "Analyzing," "Applying," "Understanding," and finally, "Remembering" at the base. This hierarchical structure reflects the increasing complexity of cognitive skills.
Bloom's Taxonomy categorizes learning outcomes into six cognitive levels: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating. This hierarchical structure, as visualized in the infographic, implies that mastery of lower levels is foundational for achieving higher levels. For example, a student cannot effectively analyze a complex craft technique without first understanding the basic principles behind it. This progression from basic knowledge recall to higher-order thinking allows you to structure learning experiences that effectively build upon previous knowledge and skills.
How Bloom's Taxonomy works:
The taxonomy uses specific action verbs associated with each cognitive level. When crafting learning outcomes examples, start with phrases like "By the end of this workshop, participants will be able to..." and then select an appropriate action verb paired with a specific task.
Examples relevant to Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners:
- Remembering: "List the five essential tools for jewelry making."
- Understanding: "Explain the difference between SEO and SEM."
- Applying: "Use a specific social media marketing strategy to promote a new product line."
- Analyzing: "Compare and contrast different pricing models for handmade goods."
- Evaluating: "Critique the effectiveness of a competitor's online marketing campaign."
- Creating: "Design a unique online marketing strategy for their handmade business."
Actionable Tips:
- Use only one action verb per learning outcome for clarity.
- Ensure outcomes are observable and measurable – you should be able to assess whether the learner has achieved them.
- Balance outcomes across different cognitive levels to foster a well-rounded learning experience.
- For Shopify store owners, focus on outcomes related to e-commerce, digital marketing, and customer service. For crafts business owners, emphasize outcomes related to specific craft skills, design principles, and business management for artisans.
When and Why to Use Bloom's Taxonomy:
Bloom's Taxonomy is invaluable for any educational endeavor, whether you're developing online courses, in-person workshops, or even simple training materials. Its structured approach helps ensure alignment between your learning objectives, teaching activities, and assessment methods.
Pros:
- Widely recognized and provides a common language for discussing learning goals.
- Promotes deeper learning beyond rote memorization.
- Helps to create more effective and measurable assessments.
Cons:
- Can be challenging to perfectly categorize interdisciplinary learning outcomes.
- Can become rigid if applied too strictly.
By using Bloom’s Taxonomy, you can ensure that your educational content, whether for your team or your customers, is strategically designed to deliver specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) learning outcomes. This framework allows you to create targeted learning experiences that empower your audience to develop relevant skills and knowledge, ultimately leading to greater success for your business and theirs.
2. SMART Learning Outcomes
SMART learning outcomes represent a highly effective approach to crafting clear, focused, and measurable educational objectives. This framework, based on the acronym SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound), provides concrete goals and standards for both educators and students, thus making assessment more straightforward and meaningful. This approach is invaluable for anyone developing educational content, including Shopify store owners creating online courses or workshops, and arts and crafts business owners designing instructional materials for their classes. SMART outcomes ensure that learning experiences are well-defined and lead to demonstrable skills or knowledge acquisition.

How SMART Learning Outcomes Work:
Each element of the SMART framework contributes to creating robust learning outcomes examples:
-
Specific: The outcome clearly defines what students should know or be able to do. Avoid vague language. For example, instead of "Students will understand pottery," a specific outcome would be "Students will be able to center clay on a potter's wheel."
-
Measurable: The outcome can be observed, evaluated, or quantified. This allows for objective assessment. For example, "Students will create a bowl with even walls, no thicker than 1/2 inch."
-
Achievable: The outcome is realistic within the course constraints and student abilities. Consider the available time, resources, and student skill levels. A beginning pottery class should not expect students to create complex ceramic sculptures in their first lesson.
-
Relevant: The outcome is connected to the overall program goals and real-world applications. Why is this skill or knowledge important? For a Shopify store owner teaching product photography, a relevant outcome would be "Students will be able to take professional-quality photos of their products for their online store."
-
Time-bound: The outcome specifies when students should achieve the desired competency. This sets a clear timeframe for learning. For instance, "By the end of this workshop, students will be able to edit product photos using Adobe Photoshop."
Examples of Successful Implementation:
-
Shopify Store Owner: "By the end of this online course, students will be able to create a five-product Shopify store, including product descriptions, images, and pricing."
-
Arts and Crafts Business Owner: "Within three hours of instruction, students will be able to knit a scarf using the basic garter stitch."
Actionable Tips for Creating SMART Learning Outcomes:
- Focus on student performance: What should students do with the knowledge or skills gained?
- Use clear action verbs: (e.g., analyze, create, evaluate, demonstrate, apply)
- Include performance standards where appropriate: (e.g., with 90% accuracy, within a specific timeframe)
- Reference specific assignments or assessments: How will you measure achievement?
- Review with colleagues or peers: Ensure clarity and objectivity.
- Test outcomes: Could a third party reliably assess student performance based on your description?
When and Why to Use SMART Learning Outcomes:
SMART learning outcomes are beneficial whenever you aim to create structured and effective learning experiences. They are particularly useful for:
- Designing online courses or workshops
- Developing training materials
- Creating lesson plans
- Assessing student progress
- Mapping curriculum development
- Ensuring alignment between teaching and learning
Pros and Cons:
Pros: Provides clear expectations, facilitates objective assessment, helps design focused teaching activities, supports continuous improvement.
Cons: Can restrict creativity if too narrowly defined, may overemphasize easily measured outcomes, time-bound aspect may not suit all learning paces.
Learn more about SMART Learning Outcomes
This method deserves its place on this list because it provides a practical and widely recognized framework for crafting effective learning outcomes examples, applicable to various educational contexts, including online businesses and craft workshops. It promotes clarity, measurability, and relevance in learning objectives, ultimately enhancing the learning experience for everyone involved.
3. Competency-Based Learning Outcomes
Competency-based learning outcomes represent a shift from traditional time-based education to a focus on demonstrable skills and abilities. Instead of measuring progress by hours spent in a classroom, competency-based learning emphasizes mastery. Students progress at their own pace, demonstrating proficiency in specific skills before moving forward. This approach ensures learners acquire essential professional or discipline-specific capabilities, making it a powerful tool for learning outcomes examples.

This model is particularly relevant for Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners who often need to acquire specific, practical skills quickly and efficiently. Imagine needing to master a new marketing technique or a specific crafting skill to boost your business. Competency-based learning allows you to focus solely on that skill, learn it at your own pace, and demonstrate mastery before moving on to other areas. It prioritizes practical, applicable skills and knowledge, often based directly on industry or professional standards. This focus ensures that the learning is relevant and directly translates to real-world application. Learn more about Competency-Based Learning Outcomes. This personalized learning pathway allows for flexible pacing, catering to different learning styles and speeds.
Several features distinguish competency-based learning: a focus on practical skills, alignment with industry standards, personalized learning pathways, progress determined by demonstrated mastery, and often, multiple levels of proficiency within each competency. For example, a Shopify store owner might demonstrate basic proficiency in social media marketing, then progress to advanced levels involving targeted advertising and analytics.
Examples of Competency-Based Learning Outcomes:
- For a Shopify store owner: "Develop and implement a successful social media marketing campaign that increases website traffic by 15%."
- For an arts and crafts business owner: "Create and photograph high-quality product images suitable for online marketplaces and social media platforms."
- Nursing program: "Administer medications safely following the five rights of medication administration."
- Software development program: "Design and implement a secure database according to industry standards."
- Teacher education: "Plan and deliver differentiated instruction to meet diverse student needs."
Pros:
- Directly prepares learners for specific workplace demands.
- Offers flexible pacing for diverse learners.
- Clearly communicates the value of the education to employers and clients.
- Reduces gaps between education and job requirements.
- Provides a clear framework for lifelong learning.
Cons:
- Assessing complex competencies can be challenging.
- Implementing competency-based learning may require significant resources.
- Risks reducing education to mere training if not carefully balanced with theoretical knowledge.
- Potential for fragmentation of knowledge into discrete skills without a broader context.
- Less emphasis on theoretical knowledge, which can be limiting in some fields.
Tips for Implementing Competency-Based Learning:
- Collaborate: Work with industry partners or experienced professionals to identify the most relevant competencies for your field.
- Authentic Assessments: Develop authentic assessments that mirror real-world applications of the skills. For example, a Shopify store owner might be assessed on their ability to actually run a successful ad campaign.
- Clear Rubrics: Create clear rubrics with multiple proficiency levels to guide learners and provide consistent evaluation.
- Diverse Resources: Provide varied learning resources (videos, articles, hands-on projects) to cater to different learning styles.
- Practice & Feedback: Design regular opportunities for practice and feedback to help learners refine their skills.
- Reflection: Incorporate reflection activities to help learners connect practical skills to broader theoretical foundations.
Competency-based learning deserves its place in this list because it offers a powerful alternative to traditional educational models. It’s particularly well-suited for individuals who need to quickly acquire and demonstrate practical skills relevant to their work, like Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners striving to improve their businesses. By focusing on demonstrable skills and personalized learning, this approach empowers learners to acquire targeted expertise and achieve specific, measurable outcomes. Institutions like Western Governors University and Southern New Hampshire University's College for America program have pioneered this approach, demonstrating its effectiveness in preparing individuals for the demands of the modern workplace.
4. Affective Domain Learning Outcomes
Affective domain learning outcomes are a crucial aspect of a holistic education, focusing on the emotional and attitudinal dimensions of learning. Unlike cognitive learning outcomes that address what students should know, affective outcomes address how students should feel, value, and interact with the content and the learning process itself. These learning outcomes examples are particularly relevant for Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners who often need to connect with customers on an emotional level, fostering brand loyalty and appreciation for their unique products.
This domain explores how learning experiences shape learners' attitudes, values, beliefs, emotions, and motivation. It recognizes that effective education involves not just cognitive development (knowing things) but also changes in perspectives, appreciation, and value systems. Understanding and applying these principles can significantly impact customer relationships and brand perception. For example, crafting a brand story that resonates with customers' values can lead to deeper engagement and increased sales.
Features based on Krathwohl's Taxonomy:
Krathwohl's taxonomy provides a framework for categorizing affective learning outcomes into five hierarchical levels:
- Receiving: The learner is open to experiencing new information or stimuli. Example: Attentively listen to diverse perspectives on customer needs. This is the foundation for building customer understanding and informing product development.
- Responding: The learner actively participates and reacts to the stimuli. Example: Voluntarily participate in online forums to discuss industry trends and customer feedback. Actively engaging with customer communities builds trust and provides valuable insights.
- Valuing: The learner attaches worth and importance to the information or experience. Example: Demonstrate commitment to sustainable practices in product creation. Highlighting values like sustainability can attract environmentally conscious customers.
- Organization: The learner integrates different values and creates a personal value system. Example: Reconcile personal artistic vision with market demand for product design. Balancing creative vision with practical business considerations is key for sustainable growth.
- Characterization: The learner internalizes the values and acts consistently based on them. Example: Consistently apply principles of fair trade in sourcing materials. This demonstrates a strong commitment to ethical practices and can resonate deeply with customers.
Pros of Using Affective Learning Outcomes:
- Acknowledges the importance of emotional engagement: For Shopify and craft business owners, understanding customer emotions is paramount. Affective outcomes help tailor marketing strategies and product offerings to resonate with the target audience.
- Develops ethical decision-making: Strong values contribute to building a trustworthy brand. This is particularly important for handmade businesses, where customers often value ethical sourcing and production.
- Supports intrinsic motivation: Passion is often a driving force for creative entrepreneurs. Nurturing this passion through affective learning can sustain long-term business success.
Cons of Using Affective Learning Outcomes:
- Challenging to observe and assess objectively: Measuring attitudes and values can be difficult, requiring creative assessment methods like reflective journals or customer surveys.
- Raises concerns about imposing values: While promoting positive values is important, businesses must be mindful of respecting individual customer beliefs and avoiding preachiness.
- Takes longer to achieve: Building trust and fostering emotional connections takes time and consistent effort.
Tips for Implementation:
- Use storytelling: Share the story behind your brand and products to connect with customers on an emotional level.
- Create interactive content: Encourage customer engagement through polls, Q&As, and social media discussions.
- Solicit customer feedback: Actively seek customer opinions to understand their values and preferences.
- Showcase your values: Highlight your commitment to ethical practices, sustainability, or community involvement.
- Build a strong brand community: Foster a sense of belonging among your customers, creating a loyal following.
By focusing on affective learning outcomes alongside cognitive ones, Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners can create a more meaningful and impactful experience for their customers, fostering stronger relationships and ultimately driving business growth. These learning outcomes examples are not just theoretical concepts but practical tools for building a successful and fulfilling business.
5. Psychomotor Domain Learning Outcomes
Psychomotor domain learning outcomes, a key aspect of crafting effective learning experiences, focus on the development of physical skills and coordination. These outcomes are essential learning outcomes examples, particularly relevant for any teaching or training that involves manual dexterity, manipulation of tools or equipment, and precise movements. From mastering a pottery wheel to expertly packaging delicate crafts for shipment, psychomotor skills play a crucial role in numerous disciplines. This domain recognizes the progressive nature of skill acquisition, acknowledging that learners move from initial observation and imitation to eventually achieving complex and nuanced performance. Understanding and implementing these learning outcomes can significantly impact the success of training programs and educational curricula for Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners.
This domain uses established frameworks, typically based on taxonomies developed by Simpson, Dave, or Harrow. These taxonomies generally outline levels of skill development, progressing from basic perception (awareness of stimuli) through set (mental preparedness), guided response (early attempts), mechanism (basic proficiency), complex overt response (skilled performance), adaptation (adjusting skills to new situations), and finally, origination (creating new movement patterns). For example, a beginner potter might start at the "guided response" level, following specific instructions to center clay on the wheel, while an experienced potter operates at the "adaptation" or even "origination" level, intuitively adjusting their technique based on the clay's consistency or inventing new decorative techniques.
This focus on observable physical performance is a defining feature of psychomotor learning outcomes. They frequently involve elements of precision, timing, and coordination. They emphasize procedural knowledge and muscle memory, reflecting the importance of repeated practice and refinement in skill development. For a Shopify store owner, this might translate into efficiently packaging orders for shipment, including securely wrapping fragile items and optimizing box size to minimize shipping costs. For an artisan crafting jewelry, psychomotor skills translate to the precise movements required for intricate metalwork or gem setting.
Pros of Using Psychomotor Learning Outcomes:
- Essential for technical and hands-on professions: This is crucial for fields like crafts, culinary arts, and many areas relevant to Shopify sellers handling and shipping products.
- Clear performance expectations: They provide a clear roadmap for skill development, outlining what learners should be able to do at each stage.
- Supports professional confidence: Mastering a physical skill enhances confidence and competence.
- Easily observable and assessable: Performance can be directly observed and evaluated using rubrics.
- Directly applicable to workplace requirements: These skills are directly transferable to real-world job tasks.
Cons of Using Psychomotor Learning Outcomes:
- Resource intensive: May require specialized equipment, facilities, and individualized instruction.
- Accessibility limitations: Physical limitations can pose challenges for some learners.
- Time commitment: Developing mastery can be time-consuming.
- Scaling challenges: Difficult to implement effectively in large class settings.
- Feedback demands: Often requires personalized demonstration and feedback.
Examples of Psychomotor Learning Outcomes:
- Ceramics: "Throw a symmetrical bowl on a pottery wheel with consistent wall thickness."
- Jewelry Making: "Set a cabochon stone in a bezel setting with a smooth and polished finish."
- Shopify Order Fulfillment: "Package and label 20 orders per hour according to shipping best practices, minimizing damage and shipping costs."
- Photography (Product Photography): "Adjust lighting and camera settings to capture professional-quality product photos that accurately represent the item's color and texture."
Tips for Implementing Psychomotor Learning Outcomes:
- Deconstruct complex skills: Break down complex skills into smaller, manageable steps.
- Clear demonstrations: Provide clear and concise demonstrations before students practice.
- Detailed rubrics: Develop rubrics with specific performance criteria.
- Self-assessment tools: Utilize video recording for student self-assessment.
- Regular practice: Schedule frequent, short practice sessions.
- Peer feedback: Incorporate peer feedback along with instructor evaluation.
- Simulation training: Utilize simulation before high-stakes, real-world application.
Psychomotor learning outcomes deserve a prominent place in any discussion of learning outcomes examples because they address the vital role of physical skills in a wide array of disciplines. They provide a structured approach for developing, assessing, and refining these skills, ultimately leading to improved performance and professional competency. This is especially relevant for Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners who often rely on precise and well-developed psychomotor skills for the creation, handling, and successful delivery of their products.
6. Threshold Concept Learning Outcomes
Threshold concept learning outcomes represent a powerful approach to curriculum design focused on transformative learning. Instead of simply listing discrete facts or skills a student should acquire, threshold concept learning outcomes prioritize deep understanding of key ideas that reshape a student's thinking within a specific discipline. These "learning outcomes examples" are particularly valuable for fostering a genuine grasp of a subject and promoting the ability to apply knowledge in new and complex contexts. This approach is relevant even for practical skills training, as it can highlight the underlying principles that allow for adaptability and problem-solving.
Threshold concepts act as gateways or portals. Once a student grasps a threshold concept, it fundamentally alters their perspective and opens up new avenues of understanding that were previously inaccessible. These concepts are often "troublesome knowledge"—ideas that students typically struggle with—but overcoming these challenges leads to significant intellectual growth. Think of it like learning to ride a bicycle: once the balance and coordination click, it transforms your ability to navigate the world on two wheels. This is a key differentiator among learning outcomes examples because it focuses on the "aha!" moment of understanding.
Features of Threshold Concept Learning Outcomes:
- Transformative Understanding: Emphasizes a shift in perspective rather than rote memorization.
- Troublesome Knowledge: Addresses concepts that students typically find difficult.
- Integrative: Connects different aspects of the discipline.
- Irreversible Change: Represents a fundamental shift in understanding that is difficult to unlearn.
- Bounded Concepts: Defines the boundaries of disciplinary thinking.
Examples of Threshold Concept Learning Outcomes:
- Economics: Analyze market scenarios using the concept of opportunity cost. (This shifts students from simply calculating costs to understanding the trade-offs inherent in every decision.)
- Literary Studies: Apply critical theory frameworks to interpret texts beyond surface meanings. (This moves students from summarizing plots to analyzing deeper themes and perspectives.)
- Physics: Use Newtonian principles to explain and predict motion, overcoming intuitive misconceptions. (This helps students move beyond everyday observations to a more scientific understanding of forces and motion.)
- Computer Science: Apply object-oriented programming paradigms to develop modular software solutions. (This allows students to think about programming in a more structured and reusable way.)
- Shopify Store Management (For e-commerce business owners): Analyze website traffic data to optimize marketing strategies and increase conversion rates. (This moves store owners from simply posting products to understanding how customers interact with their online store and tailoring their approach accordingly.)
- Arts and Crafts Business (For makers and artisans): Develop a pricing strategy that accounts for material costs, labor, and market value to ensure profitability. (This helps artisans shift from simply covering costs to understanding how to price their work for sustainable business growth.)
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Prioritizes deep understanding over breadth of content.
- Addresses fundamental misconceptions.
- Helps students think like practitioners in the discipline.
- Provides focus for curriculum design.
- Promotes meaningful transfer of learning.
Cons:
- Can be difficult to identify authentic threshold concepts.
- Challenging to assess transformative understanding.
- Can take significant time for students to grasp.
- Often involves a "liminal" period where students feel stuck.
- Less straightforward than traditional knowledge-based outcomes.
Tips for Implementing Threshold Concept Learning Outcomes:
- Identify Struggles: Pinpoint concepts where students consistently struggle.
- Multiple Approaches: Design various ways to approach the same concept.
- Safe Space for Confusion: Encourage questions and create an environment where students feel comfortable expressing their confusion.
- Visual Aids: Use visual models and analogies to support understanding.
- Diagnostic Assessments: Implement assessments that identify misconceptions.
- Extended Engagement: Allow ample time for students to grapple with difficult concepts.
- Reflection: Incorporate reflective activities where students articulate their evolving understanding.
Threshold concept learning outcomes offer a valuable approach for achieving deep learning and fostering genuine expertise. By focusing on transformative understanding of key concepts, educators can empower students to think critically, solve complex problems, and apply their knowledge in new and meaningful ways. While this approach presents certain challenges, the potential rewards make it a worthwhile consideration for any curriculum designer seeking to move beyond surface-level learning. These learning outcomes examples offer a practical roadmap to developing truly effective educational experiences.
7. Backward Design Learning Outcomes
Backward design learning outcomes represent a powerful approach to crafting effective learning experiences. This method, deserving of its place in any list of learning outcomes examples, flips the traditional instructional design process on its head. Instead of starting with activities and then figuring out how to assess them, backward design begins with the end in mind: what should students know and be able to do? This outcome-focused approach ensures that learning activities and assessments directly support the desired learning, fostering deep understanding and skill development.
How It Works:
Backward design follows three key stages:
-
Identify Desired Results: Define the ultimate goals of the learning experience. What knowledge, skills, and understandings should students acquire? These are often framed as "essential questions" that probe core concepts and "enduring understandings" that represent the big ideas students should retain long after the learning experience concludes. For a Shopify store owner creating an online course, this might involve identifying the skills needed to successfully market products online, such as understanding social media advertising or email marketing strategies.
-
Determine Acceptable Evidence: Once the desired results are clear, the next step is to determine how students will demonstrate their learning. What evidence will convincingly show that they have achieved the intended outcomes? This might include project portfolios, performance tasks, presentations, or traditional assessments. For an arts and crafts business owner teaching a workshop, this could involve students creating a finished piece demonstrating a specific technique.
-
Plan Learning Experiences: Only after defining the desired outcomes and evidence of learning do you plan the specific learning activities. These activities are intentionally designed to equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to succeed on the chosen assessments and achieve the desired learning outcomes. Learn more about Backward Design Learning Outcomes to see how sequencing plays a vital role in this process.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- History Course: Instead of simply lecturing on the Civil War, a teacher using backward design might start with the learning outcome "Analyze primary sources to develop evidence-based interpretations of historical events." Assessments could involve analyzing historical letters and documents, while learning activities might include guided practice in interpreting primary sources.
- Mathematics: Rather than just teaching formulas, a math instructor might aim for the outcome "Apply statistical methods to real-world data sets to draw valid conclusions." Students could then be assessed on their ability to analyze a real-world data set, and learning activities would focus on applying statistical methods to diverse scenarios.
- Shopify Store Marketing Course: The desired outcome could be "Develop and implement a successful social media marketing campaign for a Shopify store." Evidence could be collected through a portfolio showcasing the campaign's development and results, while learning activities could involve modules on content creation, social media platform management, and analytics tracking.
- Arts and Crafts Workshop: The outcome might be "Create a hand-thrown ceramic bowl using proper wheel-throwing techniques." The evidence would be the completed bowl itself, judged against specific criteria. Learning activities would include demonstrations, guided practice, and individual practice on the pottery wheel.
Tips for Using Backward Design:
- Start with the big picture: Define the essential questions and enduring understandings before getting into specific details.
- Focus on evidence: Clearly articulate what constitutes acceptable evidence of understanding before planning activities.
- Design for transfer: Use performance tasks that require students to apply their learning to new situations.
- Transparency is key: Share learning outcomes and assessment criteria with students from the beginning.
- Regularly review: Periodically revisit learning outcomes to ensure they remain relevant and aligned with overall goals.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Ensures assessment authentically measures intended outcomes.
- Prevents "activity-oriented" teaching without a clear purpose.
- Prioritizes content around what's most important.
- Makes learning intentions transparent to students.
Cons:
- Can be time-intensive in the planning phase.
- May feel constraining to instructors used to more flexible approaches.
- Requires clear articulation of acceptable evidence.
Why Backward Design Matters:
Backward design is a valuable approach because it ensures alignment between learning outcomes, assessments, and learning activities. This alignment promotes deeper learning and allows instructors to effectively measure whether students are achieving the intended goals. It's particularly beneficial for Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners creating online courses or workshops, as it helps them focus on delivering impactful learning experiences that translate into real-world skills and success for their students.
7 Learning Outcomes Models Compared
| Learning Outcome Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bloom's Taxonomy Learning Outcomes | Medium - structured but can be formulaic | Moderate - requires knowledge of cognitive levels | Clear cognitive progression from recall to creation | General education across disciplines | Widely accepted; promotes deep learning; measurable |
| SMART Learning Outcomes | Low - straightforward and focused | Low - easy to design and assess | Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, time-bound | Focused curriculum and performance goals | Clear expectations; objective assessment; actionable |
| Competency-Based Learning Outcomes | High - mastery-based with multiple proficiency levels | High - needs industry input and personalized pathways | Mastery of practical, applicable skills | Professional, vocational, and workforce readiness | Flexible pacing; employer-relevant; lifelong learning |
| Affective Domain Learning Outcomes | Medium to High - emotional/attitudinal focus | Moderate - needs reflective and experiential methods | Changes in attitudes, values, motivation | Fields requiring ethics, empathy, motivation | Supports motivation; ethical development; holistic |
| Psychomotor Domain Learning Outcomes | High - physical skill mastery and precision | High - equipment, facilities, one-on-one coaching | Demonstrable physical skills and coordination | Technical, hands-on professions (medicine, arts) | Clear observable skills; builds confidence; workplace-relevant |
| Threshold Concept Learning Outcomes | High - conceptual difficulty and deep understanding | Moderate to High - needs varied teaching and assessment | Transformative intellectual growth | Disciplinary foundational concepts | Deep understanding; addresses misconceptions; promotes transfer |
| Backward Design Learning Outcomes | High - requires thorough planning and alignment | Moderate - demands clear evidence and aligned activities | Aligned outcomes, assessments, and learning experience | Curriculum design focused on meaningful learning | Ensures purpose-driven instruction; transparency; curriculum coherence |
Putting Learning Outcomes Examples to Work
This article explored a range of learning outcomes examples, from Bloom's Taxonomy and SMART goals to competency-based, affective, psychomotor, threshold concept, and backward design learning outcomes. Mastering these approaches is crucial for anyone developing educational content, especially for online businesses. By understanding these frameworks, you can create targeted learning experiences that resonate with your audience and deliver measurable results, whether you're teaching a craft technique, explaining a product's unique features, or building a community around your brand. This translates directly to increased customer engagement, stronger brand loyalty, and ultimately, business growth.
These learning outcomes examples provide a foundation for crafting effective learning objectives. Consider how each framework applies to your specific needs and audience. Whether you're a Shopify store owner selling handcrafted goods or an arts and crafts business owner sharing your expertise, defining clear learning outcomes is essential for delivering value and achieving your educational goals. By carefully planning your educational content with these frameworks in mind, you empower your customers to succeed and grow, fostering a thriving community around your brand.
Ready to take your online educational initiatives to the next level? Tevello seamlessly integrates courses and communities directly into your Shopify store, making it easy to offer valuable digital products alongside your physical goods. Explore how Tevello can help you implement these learning outcomes examples and transform your customer experience by visiting Tevello today!




