Embracing the Nuances of Teaching: A Look into Various Styles
This article explores eight different types of teaching styles to help you create more effective learning experiences. Discover the pros, cons, and practical applications of each style, from Authoritative and Facilitator to Montessori and Direct Instruction. Understanding these different types of teaching styles is crucial for tailoring your approach to individual student needs, whether you're teaching a craft workshop in person or an online course through a platform like Tevello. This list will help you choose the teaching style that best suits your online or in-person classroom.
1. Authoritative Teaching Style
The authoritative teaching style is one of the most effective types of teaching styles, striking a balance between clear structure and student autonomy. In this approach, the teacher maintains their role as the authority figure while simultaneously nurturing warm and supportive relationships with students. This style involves establishing firm boundaries and expectations, but crucially, explaining the reasoning behind them. This transparency empowers students to develop independence and self-discipline within clearly defined parameters, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility for their learning.

This style works by creating a structured yet flexible learning environment. While the teacher provides clear direction and guidance, students are also given opportunities for choice and input. This balance encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as students are encouraged to understand the "why" behind the "what" of their learning. This approach can be particularly beneficial for Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners who are teaching online courses or workshops. The structure provides a framework for learners, while the autonomy allows for creative exploration and personalization, key elements in these creative fields.
Features of the Authoritative Teaching Style:
- Clear expectations and boundaries: Students understand what is expected of them academically and behaviorally.
- Warm but professional teacher-student relationships: A supportive and respectful classroom environment fosters positive interactions.
- Explanations for rules and decisions: Transparency builds trust and encourages student buy-in.
- Balance of teacher direction and student autonomy: Students are guided while also having opportunities for independence.
- Structured classroom environment with flexibility: Provides a framework for learning while allowing for adaptation and individualization.
Pros:
- Promotes student academic achievement through clear goals and expectations.
- Develops student self-discipline and responsibility by providing choices within a structured environment.
- Creates a respectful classroom environment through positive teacher-student relationships.
- Balances control with student voice, leading to increased engagement.
- Supports the development of critical thinking by encouraging students to understand the reasoning behind rules and concepts.
Cons:
- Can be challenging to maintain the balance of authority and warmth consistently.
- May require more preparation time to develop explanations and justifications for classroom procedures.
- Some students from different cultural backgrounds might interpret this style differently, requiring sensitivity and adaptation.
- Less effective for highly independent or self-directed learners who may thrive in more autonomous environments.
Examples:
- A high school English teacher who sets clear assignment deadlines but involves students in determining paper topics.
- A middle school math teacher who explains the reasoning behind formulas while maintaining classroom discipline.
- Elementary teachers who use morning meetings to establish daily expectations with student input. Shopify store owners teaching online marketing techniques could use a similar approach by outlining clear learning objectives while allowing students to choose projects that align with their specific business needs. Arts and crafts business owners can demonstrate a technique while encouraging students to explore variations and develop their own artistic styles.
Tips for Implementing the Authoritative Teaching Style:
- Establish clear classroom rules and expectations early in the year or course.
- Explain the reasoning behind decisions and expectations transparently.
- Use a warm but firm tone when addressing student behavior.
- Provide choices within structured activities to promote student autonomy.
- Regularly check in with students to gauge their understanding and address any concerns. Learn more about Authoritative Teaching Style
The authoritative teaching style deserves its place on this list of different types of teaching styles because it offers a highly effective approach that fosters both academic achievement and the development of essential life skills like self-discipline and responsibility. By balancing structure with autonomy, this style creates a positive and productive learning environment that benefits both teachers and students. The research of Diana Baumrind and Robert Marzano highlights the effectiveness of this approach, particularly in fostering positive student outcomes.
2. Facilitator/Student-Centered Teaching Style
The Facilitator/Student-Centered Teaching Style represents a significant shift from traditional, teacher-centric instruction. In this approach, the teacher acts as a guide or facilitator, fostering a learning environment where students take ownership of their education. Instead of simply lecturing and disseminating information, the facilitator encourages exploration, discovery, and collaboration. Students are empowered to ask questions, pursue their curiosity, and construct their own understanding of the material. This style recognizes that learning is an active process, and students learn best when they are actively engaged and invested in the process. This method is particularly relevant when exploring different types of teaching styles, as it emphasizes individualized learning journeys.

Features of a Student-Centered Classroom:
- Student-driven learning activities: Projects, inquiries, and explorations led by student interest.
- Teacher as guide: Mentoring, supporting, and providing resources rather than lecturing.
- Open-ended questioning techniques: Encouraging critical thinking and deeper understanding.
- Collaborative learning environments: Peer interaction, group work, and shared learning experiences.
- Personalized learning paths: Catering to individual learning styles and paces.
- Emphasis on process over product: Valuing the learning journey and skill development over just the final outcome.
Why Use a Facilitator Approach?
This teaching style is ideal for fostering deep understanding, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. It's especially valuable when teaching complex subjects or skills that require active application and experimentation. For Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners, this translates to empowering customers to learn new techniques, explore creative possibilities with your products, and develop their own unique styles. Think of workshops where participants experiment with different glazes, or online courses where students develop their own Shopify store step-by-step with your guidance.
Pros:
- Develops student independence and self-direction.
- Promotes deeper understanding through active learning.
- Enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Accommodates diverse learning styles and paces.
- Increases student engagement and motivation.
- Builds collaboration and communication skills.
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming to implement effectively.
- May be challenging for students accustomed to traditional instruction.
- Requires thoughtful preparation and classroom management.
- May appear less structured to outside observers.
- Assessment can be more complex.
Examples in Practice:
- Project-based learning units: Students explore real-world problems related to your products, like designing a marketing campaign for a new craft supply or developing a unique product line using your materials.
- Interactive workshops: Guide participants through hands-on experiences, allowing them to explore different applications of your products and develop their skills.
- Online community forums: Create a space where customers can share their creations, ask questions, and learn from each other, fostering a student-centered learning environment.
- Personalized tutorials: Offer tailored guidance and support to individual customers based on their skill levels and learning goals.
Tips for Implementation:
- Start small: Introduce student-led activities gradually, building confidence and comfort with the approach.
- Clear frameworks: Provide structure and guidance while still allowing for flexibility and exploration.
- Scaffolded support: Offer resources and assistance tailored to different learning needs.
- Peer feedback: Establish routines for constructive feedback and collaboration among learners.
- Questioning techniques: Use open-ended questions to promote deeper thinking and inquiry.
- Reflection opportunities: Encourage students to reflect on their learning process and identify areas for growth.
This student-centered approach, popularized by educational pioneers like John Dewey, Carl Rogers, and Sugata Mitra, deserves its place in the list of different types of teaching styles because it champions active learning, personal growth, and the development of essential 21st-century skills. By empowering learners to take ownership of their education, you not only facilitate deeper understanding but also cultivate a lifelong love of learning. This can be particularly effective for Shopify and arts and crafts business owners who aim to build a loyal customer base by fostering a sense of community and shared learning.
3. Demonstrator/Coach Teaching Style
The Demonstrator/Coach teaching style is a highly effective method among different types of teaching styles, especially for skill-based learning. It combines direct instruction with guided practice, creating a learning environment where the teacher acts as both an expert model and a supportive coach. This approach involves the teacher explicitly demonstrating concepts, skills, and procedures while simultaneously verbalizing their thought processes – a technique known as "think-aloud." As students begin to grasp the concepts, the teacher gradually shifts responsibility to them, providing ongoing feedback and support as they develop proficiency. This gradual release of responsibility allows students to internalize the demonstrated skills and apply them independently.

For Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners offering online courses or workshops, this teaching style is particularly relevant. Imagine teaching a complex crafting technique like macrame or a specific software skill for online store management. The demonstrator/coach method allows you to showcase the intricate steps involved while explaining your reasoning behind each action. This makes abstract concepts tangible and provides a clear roadmap for learners to follow.
Features of the Demonstrator/Coach Teaching Style:
- Explicit modeling of skills and procedures: Clear, step-by-step demonstrations.
- Think-aloud strategies: Verbalizing the thought processes behind actions.
- Guided practice with teacher support: Opportunities for students to practice with assistance.
- Gradual release of responsibility to students: Shifting from teacher-led to student-led learning.
- Frequent formative assessment and feedback: Regular checks for understanding and improvement.
- Performance-oriented learning activities: Focus on practical application and skill development.
Pros:
- Makes abstract concepts concrete through demonstration.
- Provides clear expectations for performance.
- Supports development of procedural knowledge and skills.
- Helps students internalize expert thinking processes.
- Combines structure with practical application.
- Effective for teaching complex skills and processes.
Cons:
- Can become too teacher-centered if overused.
- May not accommodate all learning styles equally.
- Time-intensive for complex skills.
- Requires teacher expertise in both content and pedagogy.
- May create dependency on teacher modeling.
Examples for Shopify & Arts/Crafts Businesses:
- A Shopify store owner demonstrating how to set up a Facebook ad campaign, explaining each step and the strategy behind it.
- An artist demonstrating a painting technique, verbalizing their brushstrokes and color choices.
- A jewelry maker showcasing the process of wire wrapping, explaining the tools and techniques while modeling the process.
Tips for Implementation:
- Plan demonstrations carefully: Highlight key principles and anticipate potential difficulties.
- Verbalize your thinking process clearly: Explain your decisions and rationale during modeling.
- Break complex skills into manageable components: Present information in digestible chunks.
- Use the 'I do, we do, you do' sequence: Gradually release responsibility to students.
- Incorporate student demonstrations: Encourage learners to showcase their developing skills.
- Provide rubrics that clarify performance expectations: Offer clear criteria for assessment.
This teaching style’s effectiveness is backed by influential figures like Albert Bandura (social learning theory), Doug Lemov ("Teach Like a Champion"), John Hattie (research on direct instruction), and Madeline Hunter (mastery teaching model). By showcasing expertise and providing guided support, the demonstrator/coach approach empowers learners to acquire practical skills effectively. This makes it a valuable inclusion within the range of different types of teaching styles.
4. Delegator/Group-Based Teaching Style
The Delegator/Group-Based teaching style stands out among different types of teaching styles by prioritizing student autonomy and collaborative learning. Instead of directing instruction, teachers employing this method act as facilitators, consultants, or resources, guiding students as they work together in groups. This approach encourages students to take ownership of their learning, developing crucial skills like teamwork, leadership, and problem-solving through authentic, real-world applications of knowledge. The teacher's role shifts from delivering information to supporting students as they navigate complex projects and challenges, intervening only when necessary.
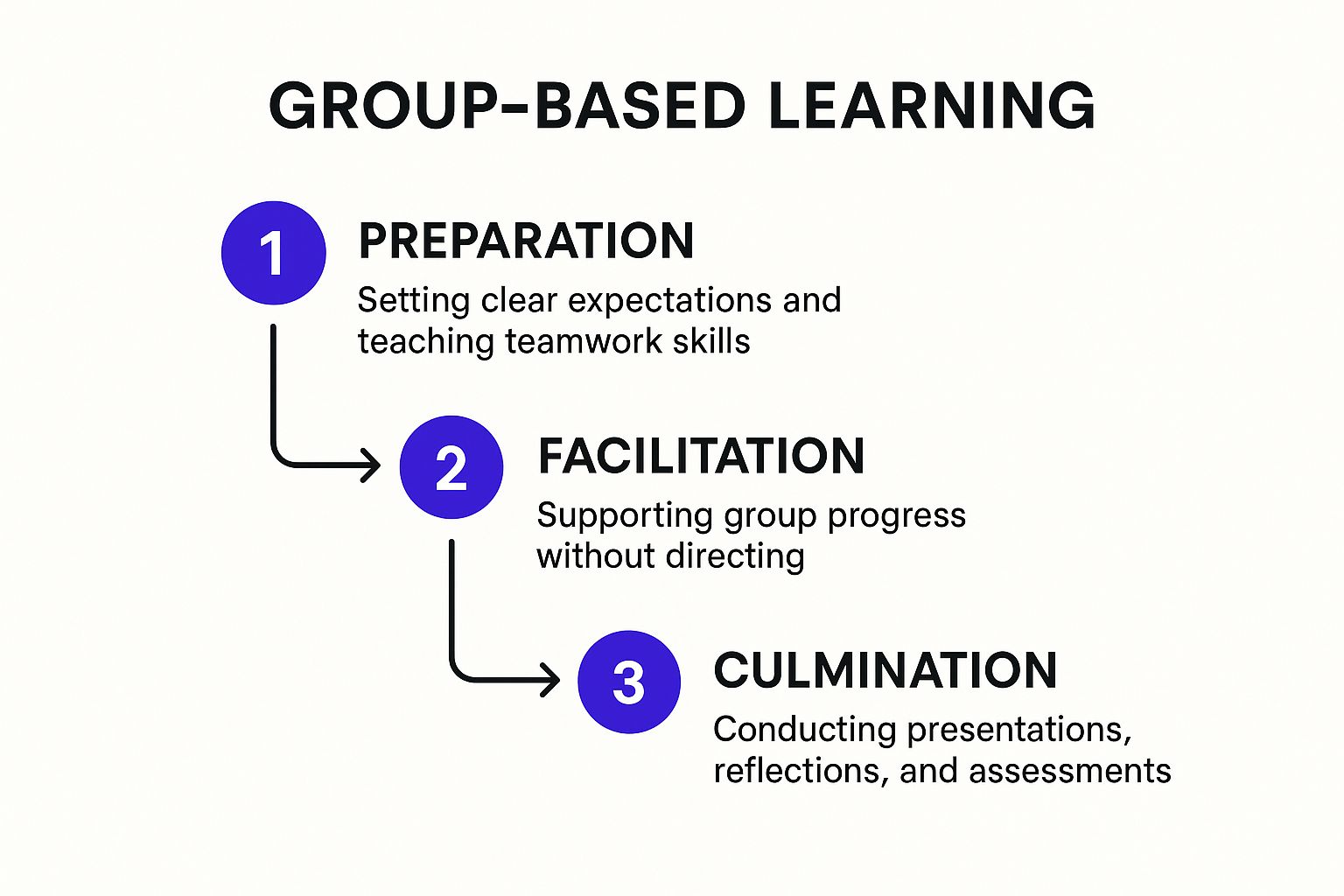
The infographic visualizes the cyclical process of the Delegator/Group-Based teaching style. It begins with the teacher presenting the challenge and establishing groups. Then, students brainstorm and research, moving on to plan and develop their solutions. Next, they present and reflect upon their work, receiving feedback and refining their understanding. Finally, the cycle repeats with a new challenge, fostering continuous growth and improvement. The infographic emphasizes the iterative nature of this style and the teacher's role as a facilitator throughout the process.
This style excels in fostering a dynamic learning environment. Features include extended group activities where students hold responsibility for both the process and the outcomes, focusing on authentic and complex problems or projects. It incorporates peer teaching and evaluation, creating multiple leadership opportunities. Think semester-long research projects, business case studies, or even a classroom economy managed by student committees. These examples highlight the practical, hands-on learning fostered by this style, which can be particularly beneficial for Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners looking to cultivate collaborative skills and innovative thinking within their teams.
The benefits are numerous, including improved collaboration and teamwork skills, preparation for collaborative workplace environments, increased student ownership and engagement, and the development of leadership capabilities and initiative. This method also promotes diverse perspectives and approaches, often leading to higher motivation. Imagine a team of craftspeople collaborating on a new product line or a group of Shopify store managers brainstorming marketing strategies. This teaching style mirrors those real-world collaborative scenarios.
However, this teaching style also has its drawbacks. It can be challenging for students lacking strong social skills, and group dynamics can sometimes lead to unequal participation. Assessing individual contributions can also be difficult, requiring careful planning and structuring. Moreover, this approach demands significant preparation from the teacher and may be perceived as less rigorous by some. Time management can become a significant issue, especially for complex projects.
To successfully implement the Delegator/Group-Based teaching style, consider these tips: establish clear group formation strategies (random, strategic, self-selected); develop explicit protocols for group function and conflict resolution; create roles to promote equal participation; build in both group and individual accountability; schedule regular check-ins and progress reports; explicitly teach collaboration skills before launching complex projects; and design reflection activities to help students process their group experiences.
This style deserves its place on the list of different types of teaching styles because it fosters essential 21st-century skills like collaboration, problem-solving, and leadership. By empowering students to take ownership of their learning and work together towards common goals, the Delegator/Group-Based teaching style creates a more engaging and ultimately more effective learning experience. Learn more about Delegator/Group-Based Teaching Style This link, while not specifically about this teaching style, explores creating online communities and boosting engagement, a relevant concept when considering the collaborative nature of group-based learning. This could be especially useful for Shopify store owners or arts and crafts business owners seeking to build online communities around their brands.
5. Hybrid/Blended Teaching Style
The Hybrid/Blended Teaching Style represents a significant evolution in modern pedagogy, earning its place among the most effective different types of teaching styles. It's not just about using technology in the classroom; it's about intentionally integrating a variety of instructional approaches, technologies, and learning environments to cater to diverse learning objectives and the unique needs of each student. This approach recognizes that a one-size-fits-all model rarely works in today's classrooms. Instead, teachers strategically select from a diverse repertoire of methods—direct instruction, student-centered activities, digital tools, and hands-on experiences—to create flexible learning pathways. The goal? To maximize engagement and learning outcomes for all learners.
How it Works:
The Hybrid/Blended Teaching Style is characterized by its inherent flexibility. Teachers utilizing this approach act as facilitators, curating learning experiences that draw on the strengths of various modalities. Imagine a classroom where students rotate through stations, engaging in direct instruction with the teacher, collaborating with peers on a project, and independently exploring concepts through interactive digital modules. This exemplifies the dynamic and multifaceted nature of blended learning.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Station Rotation: Students move between different learning stations, experiencing a mix of direct instruction, collaborative group work, and independent online learning. This is particularly effective for differentiating instruction and catering to various learning styles.
- Flipped Classroom: Students engage with pre-recorded video lectures or interactive content at home, allowing for more active, application-based activities and problem-solving during class time.
- HyFlex Courses: This model offers simultaneous in-person and remote participation options, giving students the flexibility to choose the learning environment that best suits their needs.
- Competency-Based Programs: These programs focus on mastery of specific skills and knowledge. They often utilize a blended approach, providing flexible pacing and diverse instructional resources to help students achieve competency at their own pace.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Start with clear learning objectives: Define what you want students to learn before selecting your methods. This ensures that your chosen activities align with your goals.
- Create visual roadmaps: Use charts, diagrams, or online platforms to help students navigate the blended learning experience and understand the flow of activities.
- Establish consistent routines: Clear routines for transitions between different modes of learning (e.g., online to offline) minimize disruption and maximize instructional time.
- Integrate regular feedback loops: Continuously assess the effectiveness of your blended approach through student feedback, quizzes, observations, and other assessment methods.
- Teach digital literacy: Explicitly instruct students on how to effectively utilize digital tools and navigate various online learning environments.
- Leverage learning management systems (LMS): Organize and deliver multi-modal resources, track student progress, and facilitate communication through a central online platform.
- Balance synchronous and asynchronous activities: Combine real-time interactions (e.g., live video conferences) with self-paced learning activities (e.g., online modules) to create a dynamic and engaging learning experience.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
The Hybrid/Blended Teaching Style is particularly beneficial when:
- Addressing diverse learning needs: This approach caters to different learning styles, preferences, and paces.
- Promoting student engagement: The variety inherent in blended learning can help maintain student interest and motivation.
- Developing 21st-century skills: Blended learning fosters self-directed learning, digital literacy, and adaptability—crucial skills for success in today's world.
- Offering flexible learning options: This is especially relevant for students with busy schedules or those who require alternative learning pathways.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Addresses diverse learning preferences and needs
- Provides multiple access points to content
- Maximizes engagement through variety
- Develops both teacher-directed and self-directed learning skills
- Allows for personalization while maintaining consistent standards
- Promotes adaptability in both teachers and students
Cons:
- Requires extensive planning and resource curation
- Can be complex to implement cohesively
- Demands broad pedagogical knowledge and technical skills
- May create confusion without clear communication
- Potential for superficial implementation without deep integration
While it requires careful planning and skillful execution, the Hybrid/Blended Teaching Style offers a powerful approach to creating dynamic, engaging, and effective learning experiences for all students. It acknowledges that in a world increasingly reliant on technology and demanding adaptability, education must evolve to equip learners with the diverse skills and knowledge they need to thrive.
6. Constructivist Teaching Style
The Constructivist Teaching Style stands out among different types of teaching styles because it emphasizes active learning and knowledge construction over passive reception. Instead of viewing students as empty vessels to be filled with information, constructivism sees them as active builders of their own understanding. This learner-centered approach aligns perfectly with the needs of today's learners, particularly in fields like arts and crafts where creativity and problem-solving are paramount. For Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners looking to educate their customers or train their teams, understanding this method can be incredibly beneficial. It empowers individuals to take ownership of their learning, leading to deeper understanding and more effective application of new skills and knowledge.
In a constructivist classroom, the teacher acts as a facilitator, guiding students to discover principles and build knowledge through experience, inquiry, and social interaction. Rather than presenting information as fixed truths, educators encourage students to explore, question, and develop their own meaning. This is particularly relevant for the creative process involved in arts and crafts, where individual interpretation and experimentation are key. Learning becomes a process of connecting new information to existing knowledge and lived experiences, making it more relevant and memorable. Think of a pottery class where students learn by doing, shaping the clay with their own hands and discovering the principles of form and function through experimentation.
Features of Constructivist Teaching:
- Knowledge construction rather than transmission: Learners actively build knowledge through experience.
- Emphasis on conceptual understanding over memorization: Deep understanding is prioritized over rote learning.
- Use of open-ended, authentic problems: Students grapple with real-world challenges.
- Integration of prior knowledge and experiences: Learning builds upon what students already know.
- Social learning through dialogue and collaboration: Interaction and discussion are integral parts of the learning process.
- Teacher as facilitator of discovery: The teacher guides and supports, rather than dictates.
- Reflection as a key component of learning: Students regularly reflect on their learning process and understanding.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Promotes deeper conceptual understanding.
- Develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Increases knowledge retention and transfer.
- Builds student agency and metacognition.
- Creates engaging, meaningful learning experiences.
- Honors diverse perspectives and approaches.
Cons:
- Can be time-intensive compared to direct instruction.
- May challenge students accustomed to more structured approaches.
- Requires sophisticated facilitation skills from teachers.
- May appear less organized to outside observers.
- Potential for misconceptions if not carefully guided.
- Assessment complexity due to varied student outcomes.
Examples of Constructivist Teaching in Action:
- Problem-based learning in jewelry design: Students are presented with a design challenge, such as creating a necklace for a specific occasion, and must research materials, techniques, and design principles to develop a solution.
- Collaborative painting project: Students work together to create a mural, negotiating themes, styles, and techniques through discussion and collaboration.
- Experimenting with different glazing techniques in ceramics: Students explore various glazing methods and document their findings, developing their own understanding of how different variables affect the final outcome.
Tips for Implementing Constructivist Teaching:
- Begin by eliciting students' prior knowledge and misconceptions.
- Design problems that create productive cognitive dissonance.
- Ask guiding questions rather than providing answers.
- Create structures for meaningful peer interaction and debate.
- Build in frequent reflection on both content and learning process.
- Use formative assessment to identify conceptual gaps.
- Explicitly connect constructed knowledge to formal academic concepts.
Learn more about Constructivist Teaching Style for insights into personalized learning paths, which can be a powerful tool in constructivist education. By tailoring the learning experience to individual needs and interests, you can further empower learners to take ownership of their development. This approach is especially relevant for Shopify store owners who can use personalized learning to enhance customer engagement or provide targeted training to their team. For example, a personalized learning path could guide a novice jewelry maker through the foundational skills of metalworking, while a more experienced artisan could explore advanced techniques like filigree or enameling.
By embracing the constructivist teaching style, educators and business owners alike can foster deeper learning, enhance creativity, and cultivate a more engaging and impactful learning experience. This approach is particularly well-suited to the dynamic and evolving world of arts and crafts, where continuous learning and adaptation are essential for success.
7. Montessori Teaching Style
The Montessori teaching style stands out among different types of teaching styles as a distinct child-centered approach developed by Dr. Maria Montessori. It emphasizes independence, freedom within limits, and deep respect for a child's natural psychological development. Rather than a teacher-directed model, the Montessori method empowers children to learn through self-directed activity, hands-on experiences, and collaborative play within carefully prepared environments. This approach fosters intrinsic motivation and a lifelong love of learning. While perhaps best known for its implementation in dedicated Montessori schools, understanding the core principles of this teaching style can be valuable for anyone working with children, including Shopify store owners and arts and crafts business owners seeking to engage young audiences effectively.
How it Works:
Montessori classrooms are meticulously designed learning spaces equipped with specialized materials that encourage exploration and discovery. These materials are often self-correcting, allowing children to recognize and rectify their own errors without direct teacher intervention. Mixed-age classrooms, typically spanning three years, create a dynamic learning environment where older students naturally mentor younger peers, fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility. Uninterrupted work periods, often lasting up to three hours, allow children to deeply engage with activities and develop sustained concentration. The curriculum progresses from concrete to abstract concepts, providing a solid foundation for future learning. Practical life skills, such as food preparation and self-care, are integrated into the daily routine, fostering independence and self-sufficiency.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- A child selects the pink tower from a shelf and proceeds to build it, developing visual discrimination and an understanding of dimensions.
- Older children in a mixed-age classroom assist younger peers with a challenging puzzle, strengthening both their own understanding and the younger child's learning.
- Students independently choose activities from prepared shelves, exercising their freedom of choice within the structured environment.
- A practical life station is set up with child-sized utensils and ingredients, where children learn to prepare a simple snack, developing fine motor skills and independence.
Tips for Implementing Montessori Principles:
- Observe Carefully: Pay close attention to children's individual developmental needs and interests to guide their learning experiences.
- Prepare the Environment: Create an orderly and aesthetically pleasing environment with accessible, age-appropriate materials.
- Demonstrate and Step Back: Clearly demonstrate the use of materials, then allow for independent exploration and discovery.
- Minimize Interruptions: Respect children's focused work periods and avoid unnecessary interruptions.
- Natural Consequences: Utilize natural consequences rather than external rewards or punishments to guide behavior.
- Provide Minimal Help: Offer guidance only when necessary, encouraging problem-solving and independent thinking.
- Sequential Presentation: Introduce materials sequentially, progressing from simple to complex concepts.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
- Develops intrinsic motivation and a love of learning.
- Fosters independence, concentration, and self-discipline.
- Accommodates different learning paces and styles.
- Promotes deep understanding through hands-on experience.
- Builds executive functioning skills.
- Encourages peer teaching and community.
- Develops the whole child (cognitive, social, emotional, physical).
Cons:
- Requires specialized teacher training and materials.
- Can be expensive to fully implement.
- Transition to traditional education settings may be challenging for some children.
- The less structured approach may not suit all children.
- Assessment and alignment with standardized expectations can be complex.
- Less teacher-directed instruction for specific skills development.
Why the Montessori Method Deserves Its Place:
The Montessori teaching style earns its place among different types of teaching styles due to its unique focus on child-centered learning and its proven effectiveness in fostering independence, creativity, and a lifelong love of learning. While a full implementation requires dedicated resources, understanding the core principles can inform and enhance various educational settings, including homeschooling environments and even customer engagement strategies for businesses targeting children and families. The emphasis on self-directed exploration, hands-on learning, and respecting individual learning paces offers valuable insights for anyone working with children.
Popularized By:
Dr. Maria Montessori (Italian physician and educator), Association Montessori Internationale (AMI), American Montessori Society (AMS), Montessori schools worldwide (over 22,000 globally), Celebrity advocates including Jeff Bezos, Larry Page, and Sergey Brin. While there isn't one central website, searching for "Association Montessori Internationale" or "American Montessori Society" will provide valuable resources.
8. Direct Instruction Teaching Style
Direct Instruction is a highly structured, teacher-centered approach among the different types of teaching styles, best suited for situations where clear, sequential learning of specific skills or foundational knowledge is paramount. This method emphasizes explicit teaching, carefully sequenced lessons, and frequent opportunities for guided practice with immediate feedback. Its systematic nature and focus on mastery learning make it particularly effective for novice learners or when introducing new and complex concepts. This teaching style deserves its place on the list of different types of teaching styles due to its proven effectiveness, particularly for foundational skills, and its structured approach which can provide clarity and support for both teachers and students.
How Direct Instruction Works:
The Direct Instruction teaching style operates on the principle of explicit instruction. The teacher takes the lead in presenting information clearly and directly, demonstrating procedures step-by-step, and providing ample opportunities for structured practice. The learning process is carefully sequenced, ensuring that students master one concept before moving onto the next. Frequent checks for understanding and immediate feedback are integral components, allowing teachers to address misconceptions promptly and ensure that all students are keeping pace.
Features and Benefits:
- Explicit teaching of skills and concepts: Leaves little room for ambiguity, ensuring all students receive the same core information.
- Clearly stated learning objectives: Provides transparency and sets clear expectations for learning outcomes.
- Structured, sequenced lesson format: Offers a predictable and organized learning experience, reducing cognitive load for students.
- High teacher control of content and pacing: Enables efficient delivery of information and ensures all essential material is covered.
- Frequent checking for understanding: Allows teachers to identify and address learning gaps in real-time.
- Extensive guided practice with immediate feedback: Facilitates skill development and reinforces correct application of knowledge.
- Regular assessment and reteaching as needed: Ensures mastery of key concepts before progressing to more advanced material.
- Mastery learning approach: Promotes a high level of competency and builds a strong foundation for future learning.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Efficient for teaching specific skills, clear structure, effective for novice learners and foundational skills, ensures equal access to content, reduces cognitive load, strong evidence base for effectiveness.
- Cons: Limited student autonomy, less emphasis on critical thinking and creativity, potential for reduced engagement with unskilled delivery, not ideal for all learning objectives, potential for passive learning, may not accommodate diverse learning styles.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- DISTAR (Direct Instruction System for Teaching Arithmetic and Reading) programs: Comprehensive programs designed for systematic instruction in foundational literacy and numeracy skills.
- Explicit phonics instruction in early reading: A direct approach to teaching the relationship between letters and sounds.
- I Do, We Do, You Do gradual release model: A structured framework for guiding students from teacher-led instruction to independent practice.
- Madeline Hunter's lesson design model: A widely used model emphasizing clear objectives, anticipatory set, input, modeling, guided practice, independent practice, and closure.
- Worked examples in mathematics instruction: Step-by-step demonstrations of problem-solving procedures.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Begin with clear, measurable objectives: Define exactly what students should be able to do by the end of the lesson.
- Break complex skills into manageable components: Present information in smaller, digestible chunks.
- Use concise, unambiguous language in explanations: Avoid jargon and ensure clarity in communication.
- Provide multiple examples that highlight key principles: Illustrate concepts with varied examples to promote understanding.
- Build in frequent opportunities for student response: Encourage active participation through questioning and checks for understanding.
- Check understanding before independent practice: Ensure students grasp the concepts before working on their own.
- Use error correction procedures consistently: Provide immediate and specific feedback to address mistakes.
- Maintain brisk pacing while ensuring mastery: Keep the lesson moving forward while ensuring all students are keeping up.
When and Why to Use Direct Instruction:
Direct Instruction is most effective when teaching foundational skills, introducing new and complex concepts, or working with learners who benefit from a highly structured approach. While it might not be suitable for all learning objectives or learning styles, its efficiency and clarity make it a valuable tool in a teacher's repertoire. It's particularly useful when dealing with factual information, procedures, or basic skills where mastery is essential for future learning. Though this might not be directly applicable to Shopify store owners or arts and crafts business owners in terms of classroom teaching, the principles of clear communication, structured presentation, and ensuring customer understanding are highly transferable to effective product descriptions, tutorials, and customer service interactions. Breaking down complex processes into manageable steps, providing clear examples, and offering prompt support can greatly enhance the customer experience and drive sales.
8 Teaching Styles Comparison Matrix
| Teaching Style | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements 💡 | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Authoritative Teaching Style | Moderate - balancing authority & warmth; requires prep time 🔄 | Moderate - preparation for explanations and management 💡 | Promotes academic achievement, self-discipline, critical thinking 📊 | Structured classrooms needing balance of control & autonomy 💡 | Balances clear expectations with student voice ⭐ |
| Facilitator/Student-Centered | High - demands thoughtful prep, management, and flexibility 🔄 | High - diverse materials and scaffolds to support exploration 💡 | Develops independence, critical thinking, collaboration, engagement 📊 | Ideal for inquiry, project-based, and collaborative learning 💡 | Deepens understanding through active, student-led learning ⭐ |
| Demonstrator/Coach | Moderate to High - requires modeling skill and pacing 🔄 | Moderate - materials for demos and feedback 💡 | Builds procedural knowledge, expert thinking, skill proficiency 📊 | Complex skill acquisition needing guided practice 💡 | Makes abstract concepts concrete, gradual release of responsibility ⭐ |
| Delegator/Group-Based | High - requires strong structure, group management, prep 🔄 | High - resources for projects, group facilitation 💡 | Enhances teamwork, leadership, engagement, real-world skills 📊 | Collaborative projects, authentic problems, leadership development 💡 | Promotes autonomy with teacher as consultant, real-world focus ⭐ |
| Hybrid/Blended | Very High - extensive planning, tech integration, coordination 🔄 | High - tech tools, varied instructional materials 💡 | Addresses diverse needs, maximizes engagement, student adaptability 📊 | Multiple environments combining online, face-to-face, self-directed 💡 | Flexible, personalized learning; balances modes and tools ⭐ |
| Constructivist | High - requires sophisticated facilitation, time investment 🔄 | Moderate to High - materials for inquiry and collaboration 💡 | Promotes deep conceptual understanding, metacognition, engagement 📊 | Authentic problems, social learning, discovery-based environments 💡 | Encourages active knowledge construction and critical thinking ⭐ |
| Montessori | High - needs specialized training, materials, environment 🔄 | High - specialized materials and prepared spaces 💡 | Fosters independence, intrinsic motivation, whole-child development 📊 | Early childhood mixed-age settings focused on self-directed learning 💡 | Supports natural development with hands-on, individualized learning ⭐ |
| Direct Instruction | Moderate - highly structured with sequenced lessons 🔄 | Moderate - scripted lessons and assessment tools 💡 | Efficient skills mastery, clear objectives, strong evidence base 📊 | Foundational skill teaching, novice learners, structured content 💡 | Clear, efficient teaching with strong mastery focus ⭐ |
Finding Your Teaching Style: A Path to Educational Impact
This exploration of different teaching styles—from Authoritative and Facilitator/Student-Centered to Montessori and Direct Instruction—provides a crucial foundation for crafting impactful learning experiences. Remember, the most effective approach isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. Instead, your ideal teaching style will likely be a dynamic blend, adapted to suit the unique needs of your students, the nuances of your subject matter, and the specific learning environment. Whether you're teaching a group workshop on macrame techniques or demonstrating the art of pottery through online courses, understanding these core styles allows you to tailor your approach for maximum effectiveness. As you explore these different teaching styles, remember that effective communication is key. Learning how to write clearly and concisely will significantly enhance your ability to connect with students and convey information effectively. This resource from SmartStudi offers excellent tips for success.
The key takeaway? Embrace flexibility and continuous reflection. By actively evaluating what resonates best with your audience and adjusting your methods accordingly, you can cultivate a diverse toolkit of teaching strategies. Mastering the art of blending different types of teaching styles empowers you to unlock the full learning potential of each individual you teach. This leads to more engaging workshops, more successful online courses, and ultimately, a more thriving creative business.
Ready to take your blended learning experience to the next level? Tevello provides a powerful platform for seamlessly integrating resources, fostering community interaction, and enhancing your chosen teaching style, no matter the blend. Explore Tevello today and discover how it can empower both you and your students.




